Oily Sludge Treatment and Disposal Process Introduction
 January.15,2021
January.15,2021
At present, the main processes adopted by oily sludge treatment and disposal enterprises are: quenching and tempering treatment, thermal washing, pyrolysis, thermal oxidation, incineration and preparation of flotation agent.
Enterprises will produce waste gas, waste water, sludge and noise in the process of storage, treatment and disposal of oily sludge. Waste gas, waste water and sludge need to be treated accordingly, and finally the remaining waste water and sludge should have a reasonable destination.

1. Quenching and tempering and reducing treatment process.
The main purpose of the quenching and tempering and reducing treatment process is to reduce the quantity. The main purpose of the process is to heat the oily sludge to a certain temperature, add the quenching and tempering treatment agent under stirring and react for a certain period of time. The liquid (oil-water mixture) enters the oil-water collection tank together with the upper liquid in the oily sludge storage tank.
The sludge generated after treatment shall be entrusted to other units or disposed of by itself.
1.1 main structures involved in the process.
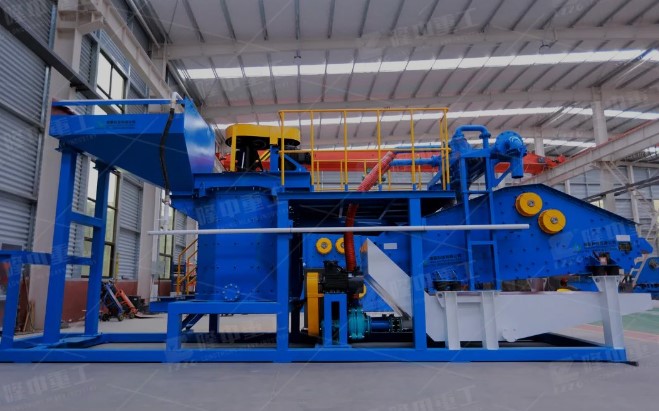
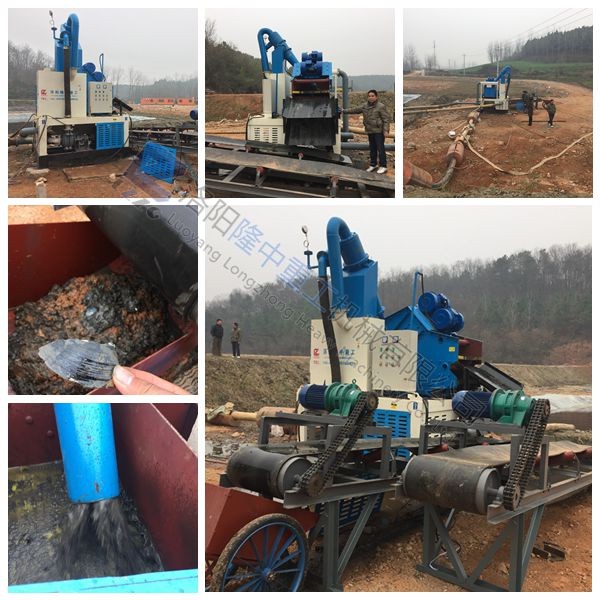
The main structures involved in the treatment process include: oily sludge storage tank, sludge lift pump, reaction tank (tank), heating furnace (heat conduction oil furnace, boiler, etc.), drug feeding system, screw stacking machine (or centrifuge), oil-water mixture collection tank, oil-water mixture transfer pump, sludge storage facilities produced after treatment.
When the waste water is reinjected after self-disposal, there should be a waste water treatment device, and the reinjection water treatment process is as follows: incoming water “adding medicine” flocculation sedimentation (or air flotation), filtration “clear water collection tank (tank)” for external transportation and reinjection.
When the wastewater is discharged into the external environment, on the basis of the above treatment process, there should also be a microbial treatment system.
1.2 main pollution production links involved in treatment and disposal.
Exhaust gas: unorganized emissions from storage facilities, unorganized hydrocarbon-containing gases discharged from reaction tanks after heating, flue gas from heating furnaces, etc.
Wastewater: oil-water mixture produced by the separation of oil-water and solid-phase substances.
Hazardous waste: waste woven bags (HW49), sludge produced after treatment (HW08), etc.
1.3 waste treatment measures and whereabouts.
Exhaust gas: the waste gas from the heating furnace shall take corresponding pollution control measures to meet the emission standards in accordance with the requirements of the EIA document.
Waste water: the oil-water mixture is sent to the oilfield joint station for treatment and reinjection after reaching the standard (with reception agreement and transfer record); when self-disposal, part of the treatment meets the oilfield reinjection water quality standard, and some is sent to the oilfield water injection station for reinjection.
The storage places of waste water and dirty oil shall be treated with anti-corrosion and anti-seepage, and a leakage liquid collection device shall be set up.
Solid waste: oily sludge storage facilities, sludge storage facilities produced after treatment shall be hardened and impervious, and there are three prevention measures and cofferdams (walls); oily sludge transported in bags, waste woven bags shall be entrusted to qualified units for treatment and disposal (with entrustment agreement); the sludge generated after treatment shall be disposed of later (receiving agreement and transfer couplet shall be required for entrusted disposal).
Risk prevention: the main production facility area, accident pool and initial Rain Water pool shall be hardened and impervious, cofferdam (wall) and waste water diversion and drainage pipe network shall be set up, and flushing wastewater, initial Rain Water and accident wastewater shall be collected and treated together with enterprise production wastewater.

2. Heating-three-phase separation process.
The main purpose of heating-three-phase separation process is to recover crude oil from oily sludge, and it is one of the technologies for resource treatment of oily sludge.
The main process is to add the oily sludge to the corresponding treatment agent and directly (or indirectly) heat the oily sludge to 80-90 ℃ with steam (or hot water), and then use a three-phase separator for three-phase separation to recover the oil; after the separated water treatment reaches the standard, part of the separated water can be reinjected; the sludge produced after treatment is entrusted to other units or treated by itself.
2.1 main structures involved in the process.
The main structures involved in the treatment process include: oily sludge storage facilities, sludge lifting pumps, dosing devices, reaction tanks, three-phase separators, oily sludge storage facilities, oily wastewater collection tanks (or collection tanks), oil recovery tanks, heating furnace (including heat conduction oil furnace, boiler, etc.).
Part of the wastewater is reused after treatment, and the remaining part should be disposed and reinjected by itself, there should be a wastewater treatment device (the treatment process is the same as the quenched and tempered treatment process); when the wastewater is discharged into the external environment, on the basis of the above treatment process, there should also be a microbial treatment system.
2.2 main pollution production links involved in treatment and disposal.
Exhaust gas: unorganized emissions from storage facilities, unorganized hydrocarbon-containing gases discharged from reaction tanks after heating, flue gas from heating furnaces, etc.
Wastewater: oily wastewater produced by the separation of oil, water and solid phase substances.
Hazardous waste: waste woven bags (HW49), sludge produced after treatment (HW08), etc.
2.3 waste treatment measures and whereabouts.
Exhaust gas: the waste gas from the heating furnace shall take corresponding pollution control measures to meet the emission standards in accordance with the requirements of the EIA document.
Waste water: part of the waste water is reused, and the rest is sent to the oilfield joint station for treatment and reinjection after reaching the standard (with reception agreement and transfer record); for self-disposal, part of the waste water is reused after the treatment reaches the oilfield reinjection water quality standard, and part is sent to the oilfield water injection station for reinjection.
The storage places of waste water and dirty oil shall be treated with anti-corrosion and anti-seepage, and a leakage liquid collection device shall be set up.
Solid waste: oily sludge storage facilities, sludge storage facilities produced after treatment, oil recovery tank area shall be hardened and impervious, and there are three prevention measures and cofferdam (wall); sludge transported in bags, the waste woven bag shall be entrusted to qualified units for treatment and disposal (with entrustment agreement); the sludge generated after treatment shall be disposed of later (receiving agreement and transfer couplet shall be required for entrusted disposal).
Risk prevention: the main production facility area, accident pool and initial Rain Water pool shall do hardening and anti-seepage treatment and set up cofferdam (wall) and waste water diversion and drainage pipe network, flushing wastewater, initial Rain Water and accident wastewater shall be collected and treated together with enterprise production wastewater.





