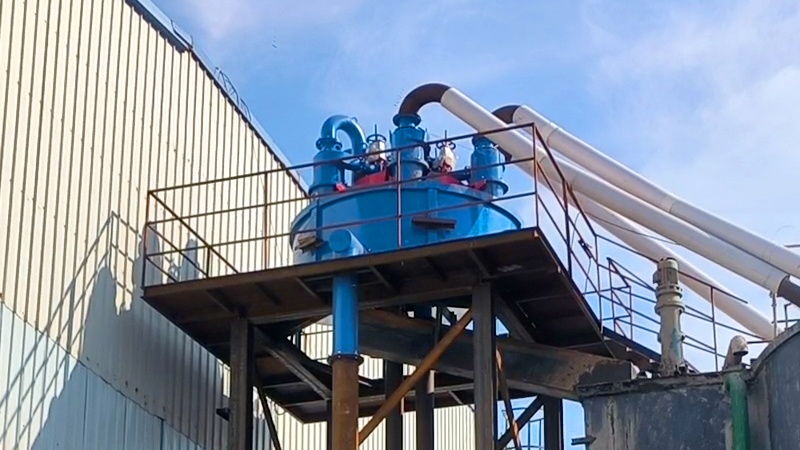
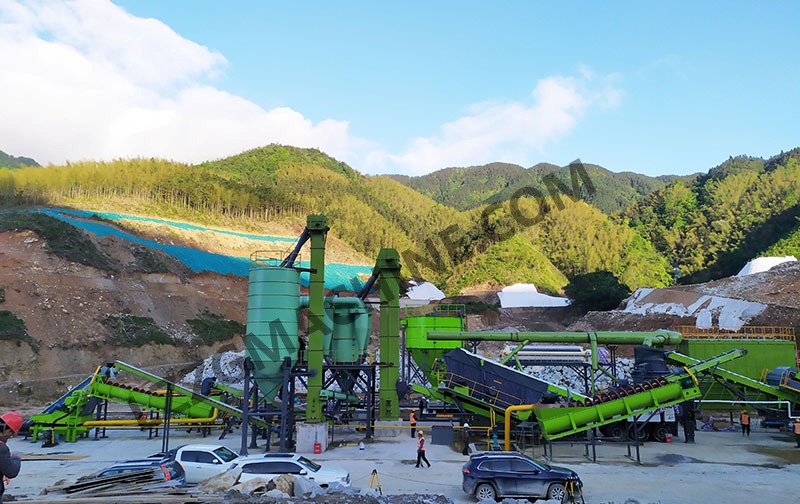
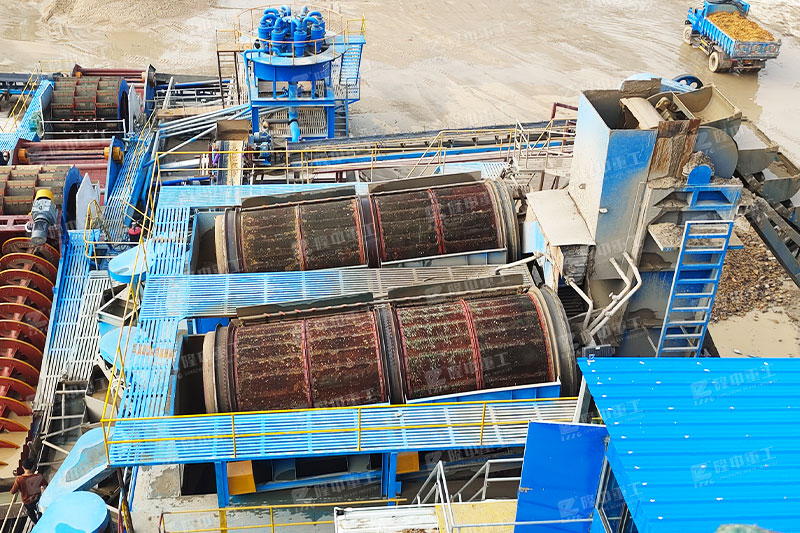
What are the impurities that affect the quality of construction sand?
 July.03,2024
July.03,2024

Mud
Refers to dust, silt and clay with a particle size of <0.08mm. These substances are attached to the surface of sand particles, hindering the combination of cement slurry and sand particles, reducing the strength of concrete. Excessive mud content will also increase the amount of concrete used; thereby increasing the shrinkage of concrete, especially when it contains clay lumps, which has a more serious impact on the quality of concrete.
Mica
Mica is flaky and has a smooth surface. It has poor adhesion to cement slurry and is easily weathered, affecting the strength and durability of concrete.
Light materials
Refers to particles with an apparent density of less than 2g/cm³, such as coal dust, shells and other materials. They also affect the strength and durability of concrete.
Sulfides and sulfates
When sand contains sulfides and sulfates such as pyrite and gypsum, it corrodes cement and reduces the durability of concrete.
Organic matter
Generally refers to humic acid and other organic acids. Organic matter also corrodes cement.
Chloride
When the chloride content of sea sand is high, it will corrode the steel bars. When sea sand is used to prepare reinforced concrete, its chloride content (converted into NaCl) should not be greater than 0.1%. For prestressed reinforced concrete, the chloride content should be strictly controlled.
When the sand contains a lot of harmful substances but must be used, it can be washed with clean water or lime water (when the organic matter content is high). If the test is qualified after washing, it can be used to comply with the principle of using local materials.





