Introduction to flocculants for wastewater treatment in sand washing plants
 June.11,2024
June.11,2024

PAC
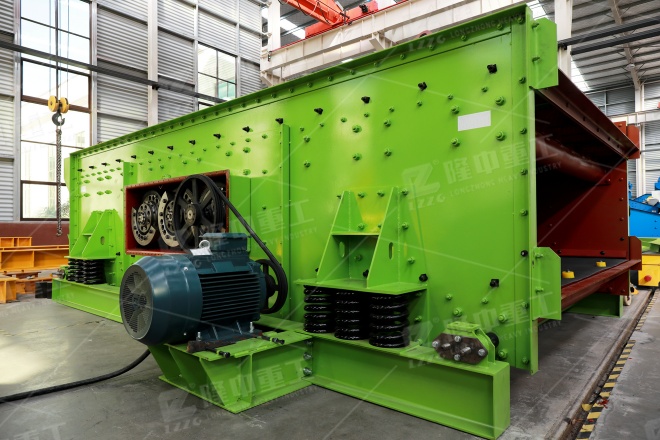
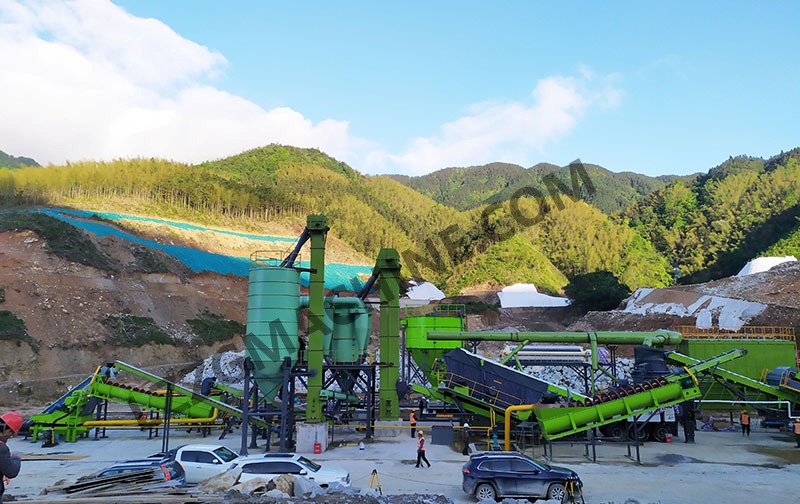
Sand washing plants produce a large amount of sewage during operation. Sand washing sewage contains a large amount of silt, impurities and suspended matter, and the turbidity of sand washing sewage is relatively high. Simple natural sedimentation is difficult to meet the needs of daily production, but direct discharge without treatment will cause environmental pollution and have a great impact on environmental protection. Therefore, sand washing sewage must be properly treated. The treated sewage can not only be recycled, but also the precipitated sediment produced after treatment can be landfilled after being treated by a filter press without causing pollution.

PAM
By comparison, it is found that the use of inorganic flocculant polyaluminum chloride PAC (commonly referred to as “yellow medicine”) combined with polymer flocculant polyacrylamide PAM (commonly referred to as “white medicine”) for sand washing wastewater has a better effect. Both have a long molecular chain structure and can react with impurities in sand washing wastewater to form colloids, which aggregate into large and dense flocs and quickly precipitate. The supernatant of sand washing wastewater after flocculation purification is clear and transparent and can be completely recycled. The precipitated flocs after precipitation are introduced into the filter press through a pipeline. The mud and sand are completely filtered out. After mud pressing, the filtered mud and sand will form a mud cake with extremely low water content.





