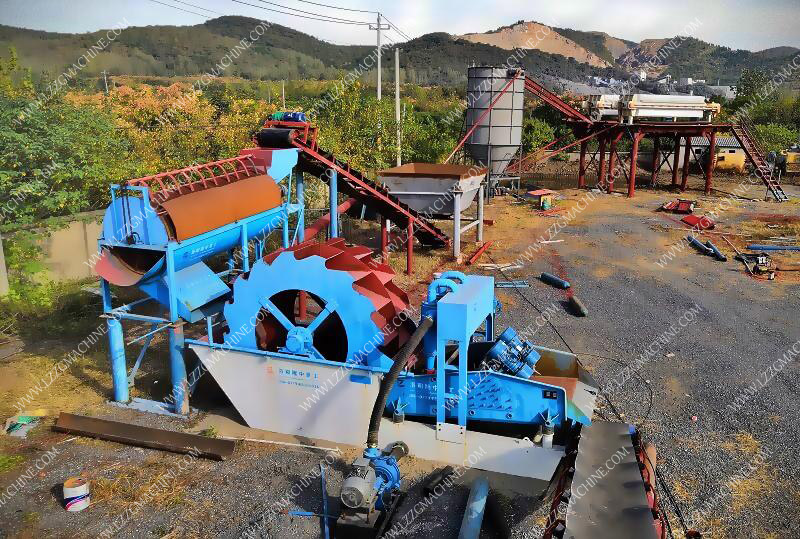
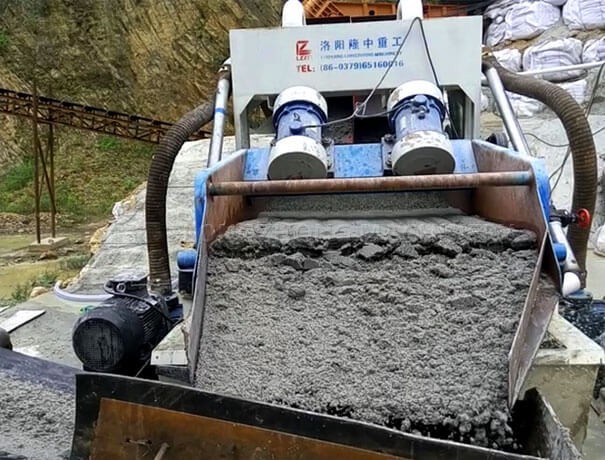
Reducing mud content in sand without washing sand
 October.24,2020
October.24,2020
The mud content of sand and gravel is more complicated, and it is not appropriate to use a simple and constant index to solve it. We believe that according to the different status and composition of sand and gravel mud content, different types of concrete should be set differently to adapt to various specific conditions.
Our regulations on the content of sand and gravel only give an economically reasonable limit in most cases. For sand and gravel that does not meet the standard requirements, it is also advisable to take some measures according to local conditions and meet the requirements. The knowledge and use of ultra-fine sand and mountain sand are the best examples.
When the mud content in the aggregate exceeds the prescribed standard and obviously affects the quality of the concrete, corresponding effective measures should be taken according to the specific situation. In the past, flushing was generally used as a common method, but this was not economical and reasonable in many cases. First, flushing requires a certain amount of manpower, consumes a lot of water, and sometimes requires additional equipment. Flushing can also cause the loss of sand and gravel and pollute the environment, and because the water content of the sand is often changed, it is not conducive to effective water control. Ash ratio. In cold areas, the freezing of sand washing will also cause construction difficulties. When the degree of washing is improperly controlled, a large amount of particles below 0.15mm in the sand will be washed away, which will damage the good gradation of the sand, and sometimes adversely affect the workability and strength of the concrete. Therefore, washing cannot be regarded as a foolproof way to deal with the mud content of sand and gravel. Others such as using high-grade cement, adjusting sand: rate, appropriately increasing the amount of cement, strengthening mixing and vibrating, mixing coarse sand, preparing low water-cement ratio and low fluidity concrete, strengthening surface pressure and curing, mixing with admixtures, and appropriately increasing The method and application of pre-stress to offset the loss of pre-stress caused by shrinkage and creep caused by mud content can be selected and used according to specific conditions.

The clear water sand is formed by alluvial granite weathered and melted by ice and snow. Due to seasonal changes in river water, the mud content in the sand often changes with the location of the sand field and the depth of collection, generally within the range of 3-10%, sometimes even Contains a lot of clay lumps, often exceeding the standard specified value. After a series of tests and analyses, the following effective measures have been taken:
① The incoming sand should be inspected frequently, piled up in different zones according to the mud content, and used separately. Use sand with higher mud content in low-grade concrete or masonry mortar, and use sand with lower mud content in high-grade concrete;
②When preparing high-grade concrete with sand with a slightly higher mud content (5~7%), reduce the sand rate, increase the amount of cement appropriately, or wash the stone without washing the sand (because washing stone is more convenient than washing sand), and appropriately extend the mixing time , Strictly control the water consumption, prepare low-flow (semi-dry) concrete and other measures, as long as the water-cement ratio is not increased, the strength of the concrete will not decrease.
③It is not allowed to use sand with high mud content (7-10%) to prepare high-grade concrete, as long as there is no special requirements such as anti-wear and frost resistance, water-reducing agents can be added to improve fluidity and reduce water consumption. (For example, with M water reducing agent, the cost of concrete will only increase by 0.6 yuan per m°, which is much lower than the cost of sand washing);
④ When using sand with a mud content of more than 3% to prepare concrete with special requirements such as abrasion resistance and frost resistance, a dry screen can be used to increase the amount of coarse sand to reduce the mud content, or use the elutriation method when conditions permit. For sand with more mud content than specified, try not to use it in concrete, or use it in low-grade concrete or masonry mortar after sieving.





