Mining tailing water cleaning and reuse system
 August.07,2020
August.07,2020
Tailings are crushed and ground rock particles produced and disposed of in the form of slurry, and are usually regarded as the final product of mineral processing, that is, the remaining waste after beneficiation or extraction of useful minerals.
According to the basic physical characteristics of tailings, tailings are divided into four categories.
(1) Soft rock tailings. Mainly produced by shale-type ore, including fine coal waste residue, trona insoluble matter, etc. Although these tailings contain a certain amount of sandy particles, the clay properties of the tailings mud significantly affect the physical properties and state of the tailings as a whole.
(2) Hard rock tailings. Mainly include lead, zinc, copper, gold, silver, molybdenum, nickel, cobalt, tin, tungsten, chromium, titanium and other types of ores.
(3) Fine tailings. It contains little or no sandy particles, including phosphate clay, bauxite red mud, iron fine tailings, and sludge in asphalt sand tailings.
(4) Coarse tailings. This type of tailings includes coarse-grained tailings of tar sands, uranium ore, gypsum, coarse iron tailings and phosphate sand tailings.
Mine Water Treatment And Recycling
After the tailings are piled up, if they are not well managed, they will cause heavy pollution to the surrounding land and rivers, and even tailings dam failures will occur.
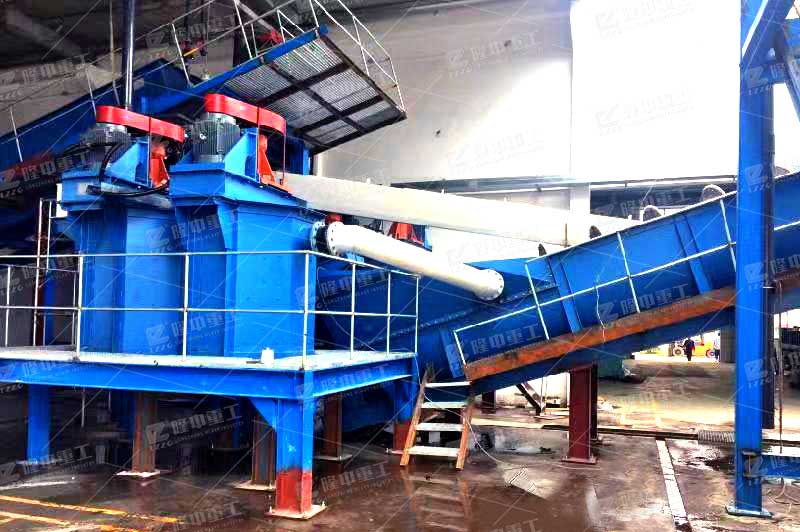
Mining tailing water cleaning and reuse system is designed for the recycling and reuse of metal and non-metal tailings and improving resource utilization. It is committed to solving the problems of solid waste generated in the washing process and the purification and reuse of sand washing tail water. The entire system is manufacturable Good, the material screening rate is high, and all the tail water is reused, which greatly improves the resource utilization rate.
Major equipment

Screening equipment: Tailings dewatering screen or tailings dry discharge system can be used to dehydrate and classify materials.

Concentration tank: Separation of mud and water through concentration and sedimentation, and purification of tail water.

Filter press: The thickened sludge in the thickening tank is pressed into a sludge cake through the filter press to achieve sludge dewatering and dry stacking.





