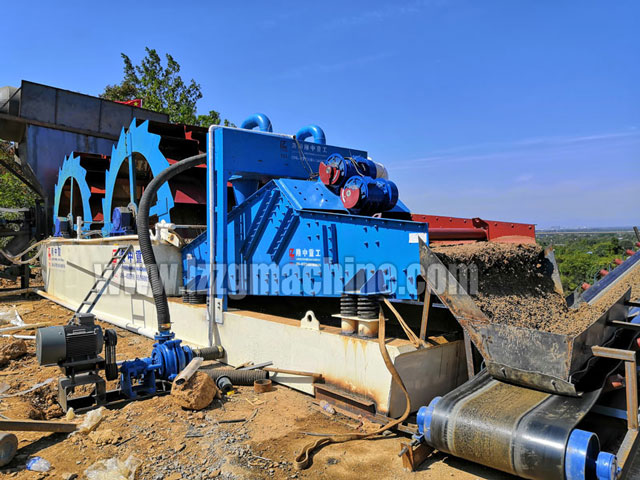
Tailings and concentrate dewatering after wet selection of magnetite
 September.11,2019
September.11,2019
The wet selection of magnetite tailings
After the wet selection of magnetite, it is divided into tailings and concentrates. The output of tailings is determined according to the ore grade, concentrate grade and the process used in the beneficiation. When the ore grade is better, the tailings output is lower; the higher the concentrate grade, the lower the tailings output; the more reasonable the process of magnetite wet selection, the less mechanical loss during the period, and the fewer tailings.

For example, when the ore is 20-grade pure magnetite, the selected concentrate grade is 72.4, that is, when the iron trioxide ore in the iron ore is all selected, one ton of ore produced by the ore is produced. It is 0.724 tons, corresponding to 0.276 tons of concentrate. Of course, in actual production, without the concentrate and tailings dehydration, the weight of concentrate and tailings plus 15 or so of water, so the magnet The tailings and concentrate dehydrated magnetite after wet selection of mines are very important for tailings and concentrate dehydration after wet selection!
Concentrates derived from wet beneficiation contain large amounts of water, which is not suitable for direct use or continued processing (such as smelting) of concentrates. Moisture in the concentrate can also cause difficulties in transportation and handling, and increase transportation costs. In areas where water is scarce, it is more necessary to return the water from the recycled mineral processing products (concentrate and tailings) to reuse (backwater) to reduce the consumption of industrial water. The process of removing water from the tailings and concentrates after wet selection of magnetite is called dehydration. The main methods of dewatering are natural drainage, concentration, filtration, and drying. Dewatering of coarsely drawn materials is relatively easy, and natural drainage is generally used. This method is excreted by the gravity of water itself. However, the method of natural drainage of materials not only slows the dehydration process but also the fine or fine mud materials will be lost with water.

Therefore, the dehydration of concentrate after wet selection of magnetite is more complicated, and it is generally completed in several stages. For example, to reduce the moisture in the concentrate after wet selection of magnetite from 60-80% to 3-8%, it is usually done through three connected dehydration stages: first, dewatering and sieving, reducing the water to 40. ~50%; then concentrated to reduce the water to 10-20%; finally, by filtration, the flotation concentrate with a moisture content of 3 to 8%. The dehydration process can be completed by three operations of dewatering screening, concentration, and filtration. However, what dewatering operation is used for a specific material depends on the nature of the material (such as particle size, magnetic properties, specific gravity, and slurry viscosity) and the moisture requirements for the dewatered ore.

LZZG’s dewatering equipment includes mining dewatering screens, high-efficiency deep cone concentrators, and filter presses. The deep cone concentrator is a solid-liquid separation device based on gravity sedimentation. When working, the solid particles suspended in the slurry in the vertebral body of the concentrator are settled under the action of gravity, and the upper part becomes clarified water so that the solid-liquid can be separated to achieve the purpose of dehydration.
The belt filter press is an efficient dewatering process for urban, industrial, mining and aggregate wastewater treatment. It is especially suitable for the dehydration of tailings such as iron ore, copper ore, lead-zinc ore, fluorite ore, bauxite or rare earth ore. The box filter press is squeezed through the plate frame so that the water in the sludge is discharged through the filter cloth to achieve the purpose of dehydration. The above three dewatering equipment used for concentration and filtration of tailings and concentrates after desiccated by tailings after wet selection of magnetite.
Advantages of tailings dewatering screen
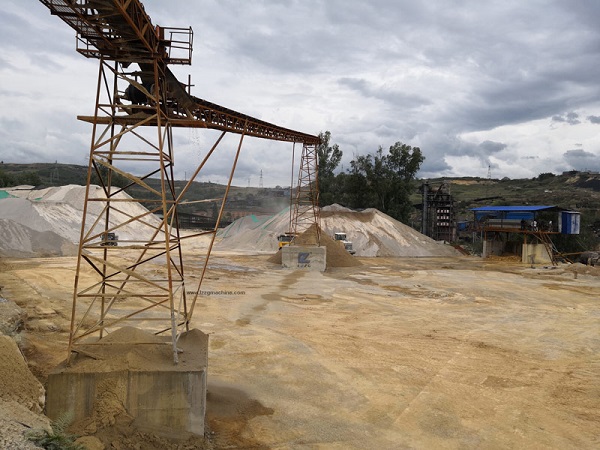

Compared with the ordinary linear vibrating screen, the tailings dewatering screen has the advantages of large processing capacity, good dewatering effect, low moisture content of the finished product after dewatering, wide application industry and high-cost performance. A tailings dewatering screen combined with the characteristics of metal tailings and specially developed a vibrating screen for dry tailing of metal tailings. It is suitable for materials with small particle size, such as fine sand, tailings, and tailings. It is mainly used for dehydration of iron ore, copper, gold and aluminum mine tailings. It is a new type of high-efficiency tailings recovery equipment designed for many problems in China’s large number of tailings dry sieves after sufficient demonstration and investigation.
The dewatering of the tailings after the wet selection of magnetite is completed by the tailings dewatering screen. The principle is that the feed tailings are uniformly fed into the inlet of the sieve by the feeding box (or cyclone), first in the horizontal At the 45-degree installation of the drain screen, about 1/3 of the moisture is removed, and after entering the joint of the flat sieve plate and the inclined sieve plate, the accumulation of materials occurs, and the material particles settle by gravity, and a thin filter layer is formed. The filter layer, in turn, prevents the remaining particles from passing through the screen, causing the filter layer to gradually thicken. The water that fails to pass through the sieve forms a pool in the upper part of the filter layer. Since the filter layer is thinner here, the water gradually removes under strong motion. Due to the high-frequency and low-amplitude vibration state, the tailings vibrating the filter layer is formed. More and more compact, and vibrate to the discharge opening, the material forms a filter cake, the water in the material is removed from the sieve surface, and the other surface appears on the surface of the layer due to capillary action. It will not overflow from the discharge opening, and the surface water will flow to the joint pool to complete the material dewatering operation.
In short, for the treatment of tailings and concentrate dehydration after magnetite wet selection, it is necessary to take its essence and go to its dregs. If you want to know the treatment technology and method of tailings and concentrate dehydration after magnetite wet selection, you can contact customer service or come to the factory for on-site inspection.





